@Real-time Personalization using Embeddings for Search Ranking at Airbnb
[[Abstract]]
- Search Ranking and Recommendations are fundamental problems of crucial interest to major Internet companies, including web search engines, content publishing websites and marketplaces. However, despite sharing some common characteristics a one-size-fitsall solution does not exist in this space. Given a large difference in content that needs to be ranked, personalized and recommended, each marketplace has a somewhat unique challenge. Correspondingly, at Airbnb, a short-term rental marketplace, search and recommendation problems are quite unique, being a two-sided marketplace in which one needs to optimize for host and guest preferences, in a world where a user rarely consumes the same item twice and one listing can accept only one guest for a certain set of dates. In this paper we describe Listing and User Embedding techniques we developed and deployed for purposes of Real-time Personalization in Search Ranking and Similar Listing Recommendations, two channels that drive 99% of conversions. The embedding models were specifically tailored for Airbnb marketplace, and are able to capture guest’s short-term and long-term interests, delivering effective home listing recommendations. We conducted rigorous offline testing of the embedding models, followed by successful online tests before fully deploying them into production.
论文解决问题:
数据稀疏情况下如何进行训练?
- 稀疏 id 聚类处理
将 user id 和 listing id 聚合成 user type、listing type
word2vec 中加入 booked listing 作为 global context
目标函数
$$\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}} \sum_{(l, c) \in \mathcal{D}{p}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{-\mathbf{v}{c}^{\prime} \mathbf{v}{l}}}+\sum{(l, c) \in \mathcal{D}{n}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{\mathbf{v}{c}^{\prime} \mathbf{v}{l}}}+\log \frac{1}{1+e^{-\mathbf{v}{l}^{\prime} \mathbf{v}_{l}}}$$
booked listing 是正样本,所以有一个负号。由于只有一项,所以没有 sigma 符号。
原始负采样是在全体样本中随机选择,业务特殊性,在正样本同一市场的样本中负采样。更好能发现同一市场中内部 listing 的差异。
new listing 通过附近 3 个同类型、相似价格的 listing embedding 进行平均。
word2vec 方法本来是无监督的,通过引入 booked listing 以及 reject 信息传递部分监督信息
利用 booked 数据训练时,文章中提到 user type 和 listing type 要在同一个空间,不知道为什么下面要有两个公式,以及 c 的含义是什么?
$$\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}} \sum_{\left(u_{t}, c\right) \in \mathcal{D}{b o o k}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{-v{c}^{\prime} v_{u_{t[[}}}}]]+\sum_{\left(u_{t}, c\right) \in \mathcal{D}{n e g}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{v{c}^{\prime} v_{u_{t[[}}}}]]$$
$$\underset{\theta}{\operatorname{argmax}} \sum_{\left(l_{t}, c\right) \in \mathcal{D}{b o o k}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{-\mathrm{v}{c}^{\prime} \mathrm{v}{l{t[[}}}}]]+\sum_{\left(l_{t}, c\right) \in \mathcal{D}{\text {neg}}} \log \frac{1}{1+e^{v{c}^{\prime} \mathrm{v}{l{t[[}}}}]]$$
embedding 之间直接对比需要在相同的向量空间。根据上面的计算可以生成一个特征 UserTypeListingTypeSim。
在如何在实时模型中引入 embedding 特征:根据一些规则收集一些 listing,计算这些 listing embedding 的平均值,再和当前排序的 lisitng 计算一个相似度,做为一个特征放到模型中。
如何评估按上面方法生成的 emb sim 特征重要性?利用 GBDT?
[[冷启动]] listing embeddings
- 找方圆 10 英里之内的 3 个最相似的 listing,取 listing embedding 的平均
使用 Embedding 方法要考虑的问题:#card
- 希望Embedding表达什么,即选择哪一种方式构建语料
- 如何让Embedding向量学到东西
- 如何评估向量的效果
- 线上如何使用
基于 [[向量化召回统一建模框架]] 角度理解
如何定义正样本 #card
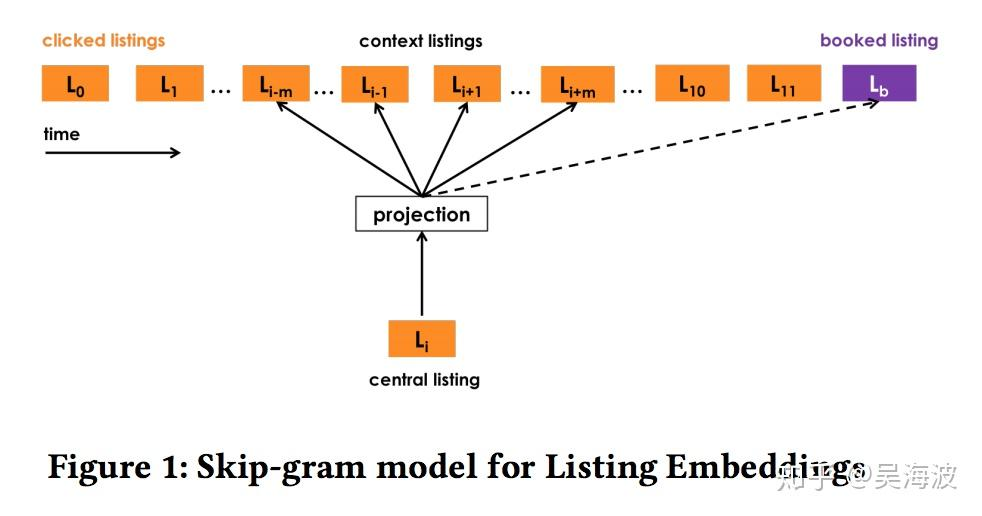
如同前边分析的那样,给定 $t$ 个用户点击的房屋(Airbnb叫 listing)序列,序列内部的房屋,其两两之间都应该是相似的。
但由于两两组合太多,因此仿照Word2Vec采用滑窗,认为某个房屋 I 只与窗口内的有限几个房屋 $c$ 是相似的。
但是,如果一个点击序列最终导致某个房屋 $l_b$ 成功预订,则 $l_b$ 业务信号非常强,必须保留。
因此,Airbnb还额外增加了一批正样本,即点击序列中的每个房屋 I 与最终被成功预订的房屋 $l_b$ 是相似的。
如何定义负样本 #card
根据召回的一贯原则,随机采样得到的其他房屋肯定是主力负样本。
但是民宿中介的业务特色决定了,在一个点击序列中的房屋(即正样本)基本上都是同城的,而随机采样得到的负样本多是异地的。
如果只有随机负采样,模型可能只使用“所在城市是否相同”这一粗粒度差异来判断两房屋相似与否,导致最终学到的房屋句量按所在城市聚类,而忽视了同一城市内部不同房屋的差异。
为了弥补随机负采样的不足,Airbnb还为每个房屋在与其同城的其他房屋中采样一部分作Hard Negative, 迫使模型关注所在城市之外的更多细节。
如何使用 embedding #card

如何定义损失函数 #card

从[[向量化召回统一建模框架]] 来理解从用户类别到房屋类别的召回
如何定义正样本 #card

如何负样本 #card

如何 embedding #card

如何定义损失函数 #card