@Temporal Fusion Transformers for Interpretable Multi-horizon Time Series Forecasting
核心贡献
- Temporal Fusion Transformer 框架 #card
recurrent layers for local processing
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: yellowinterpretable self-attention layers for long-term dependencie
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: yellow
+ specialized components to select relevant features
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: yellow
+ a series of gating layers to suppress unnecessary components
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: yellow
- 模型可解释性 interpretable insights into temporal dynamics
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: yellow
#card
+ 区分全局重要特征 globally-important variables for the prediction problem
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 3
hl-color:: yellow
+ 持久的时间模式 persistent temporal patterns
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 3
hl-color:: yellow
+ 显著事件 significant events
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 3
hl-color:: yellow
核心问题
- #card [[Multi-horizon Forecasting]] 包含复杂的输入特征组合 contains a complex mix of inputs
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: green
+ 静态变量
+ 与时间无关的静态变量 including static (i.e. time-invariant) covariates
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: green
+ 时变变量 Time-dependent Inputs
+ 已知未来输入 known future inputs,
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: green
+ 未来节假日信息
+ 外生时间序列 exogenous time series that are only observed in the past – without any prior information on how they interact with the target.
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: green
+ 历史顾客流量 historical customer foot traffic
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: green
+ 相关示意图
+ [:span]
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: yellow
使用 attention 机制增强 :-> 选择过去相关特征 used attention-based methods to enhance the selection of relevant time steps in the past
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: yellow之前基于 DNN 方法的缺陷 #card
没有考虑不同类型输入特征 fail to consider the different types of inputs
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: blue- 万物皆时序 构建模型时,将所有的特征按 time step 直接 concat 在一起,所有变量全部扩展到所有的时间步,无论是静态、动态的变量都合并在一起送入模型。
假定所有外生输入都已知与未来 assume that all exogenous inputs are known into the future
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: blue
+ 忽略重要的静态协变量 neglect important static covariates
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 2
hl-color:: blue
+ 通常处理方法是预测时和其他时间相关特征连接
- 已有深度学习方法是黑箱,如何解释模型的预测结果?#card
- do not shed light on how they use the full range of inputs present in practical scenarios
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 1
hl-color:: blue
- do not shed light on how they use the full range of inputs present in practical scenarios
相关工作
[[@A Multi-Horizon Quantile Recurrent Forecaster]] Multi-horizon Quantile Recurrent Forecaster MQRNN 结构,同时预测未来多个时间步的值
deep state space 状态空间模型,统计学,hybrid network,类似工作 [[ESRNN]] [[N-BEATS]]
-
- post-hoc methods 事后方法(因果方法),不考虑输入特征的时间顺序 do not consider the time ordering of input features
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 3
hl-color:: blue
+ [[LIME]]
+ [\[\[SHAP\]\]](/post/logseq/%40A%20Unified%20Approach%20to%20Interpreting%20Model%20Predictions.html)
+ 基于 attention 的架构对语言或语音序列有很好的解释,但是很难适用于多维度预测 attention-based architectures are proposed with inherent interpretability for sequential data
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 3
hl-color:: blue
解决方法
[[Multi-horizon Forecasting]]
prediction intervals [[区间预测]] #card
- [[DeepAR]] 直接修改模型的输出,模型不拟合原始标签,而是拟合人工指定的分布,通过蒙特卡洛采样取平均得到最终的点预测。
分位数回归 [[Quantile Regression]],每一个 time step 输出 $10^{th}$ $50^{th}$ $90^{th}$ #card
不同分位数下预测能够产生预测区间,通过区间大小反应预测结果的不确定性。某个点在不同分位数线性回归的预测结果很接近,则预测确定性搞。
Quantile Outputs
$\hat{y}i(q, t, \tau)=f_q\left(\tau, y{i, t-k: t}, \boldsymbol{z}{i, t-k: t}, \boldsymbol{x}{i, t-k: t+\tau}, \boldsymbol{s}_i\right)$
设计 [[quantile loss]]
$\begin{gathered}\mathcal{L}(\Omega, \boldsymbol{W})=\sum_{y_t \in \Omega} \sum_{q \in \mathcal{Q}} \sum_{\tau=1}^{\tau_{\max }} \frac{Q L\left(y_t, \hat{y}(q, t-\tau, \tau), q\right)}{M \tau_{\max }} \end{gathered}$
- $Q L(y, \hat{y}, q)=q(y-\hat{y}){+}+(1-q)(\hat{y}-y){+}$ #card
q 代表分位数
$()_+ = \max (0,)$
假设拟合分位数 0.9
- $Q L(y, \hat{y}, q)=q(y-\hat{y}){+}+(1-q)(\hat{y}-y){+}$ #card

+ $Q L(y, \hat{y}, q=0.9)=\max (0.9 *(y-\hat{y}), 0.1 *(\hat{y}-y))$
+ $y-\hat{y} \gt 0$ 模型预测偏小,Loss 增加更多
+ loss 中权重 9:1,模型倾向预测出大的数字,Loss 下降快
+ 假设拟合分位数 0.5,退化成 MAE
+ $Q L(y, \hat{y}, q=0.5)=\max (0.5 *(y-\hat{y}), 0.5 *(\hat{y}-y)) = 0.5*|y-\hat{y}|$
+ q-Risk 避免不同预测点下的预测量纲不一致问题,对结果做正则化处理。目前只关注 P50 和 P90 两个分位数 #card
+ $q$-Risk $=\frac{2 \sum_{y_t \in \tilde{\Omega}} \sum_{\tau=1}^{\tau_{\max }} Q L\left(y_t, \hat{y}(q, t-\tau, \tau), q\right)}{\sum_{y_t \in \tilde{\Omega}} \sum_{\tau=1}^{\tau_{\max }}\left|y_t\right|}$
模型结构
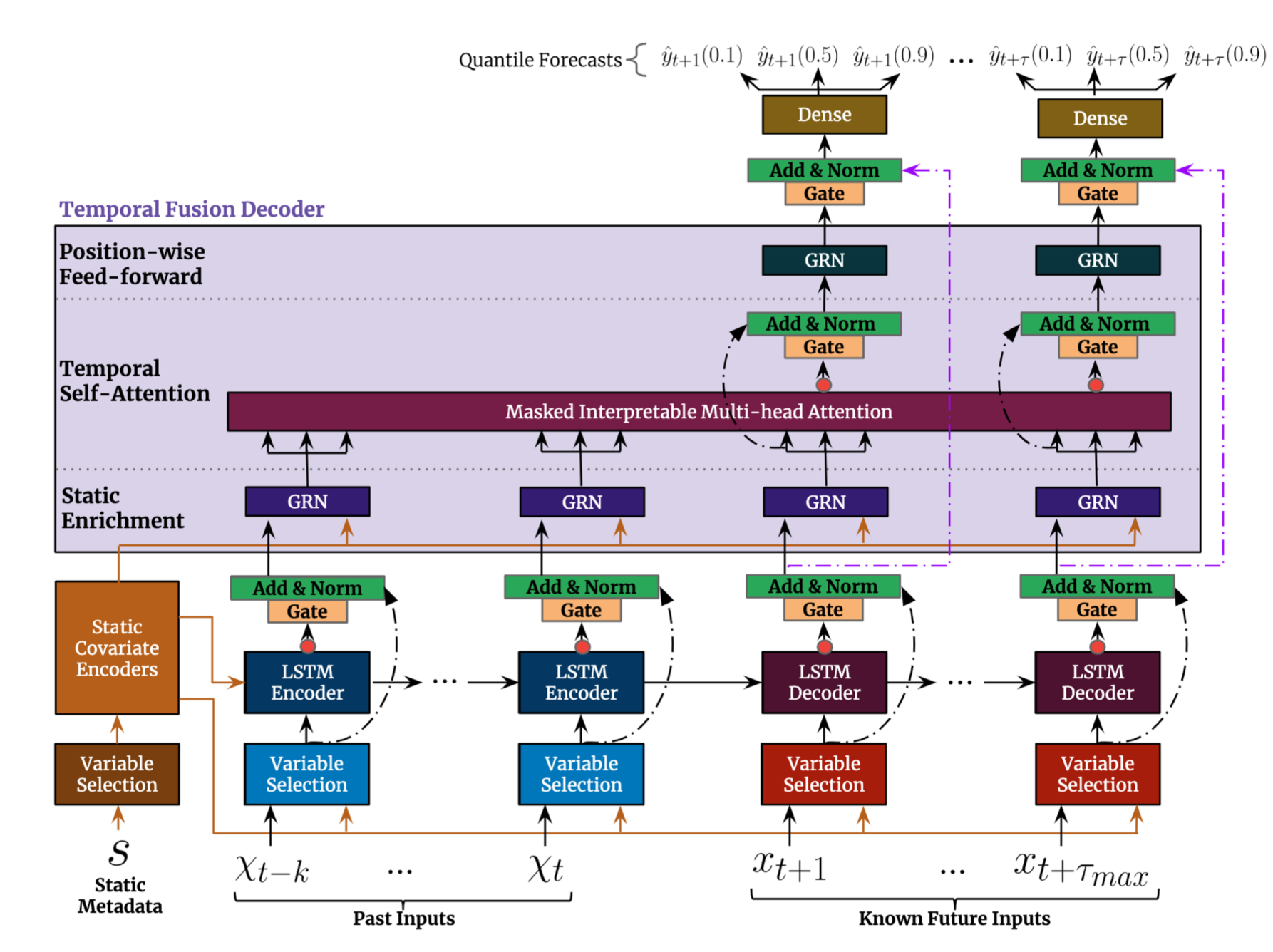
occlusion:: eyIuLi9hc3NldHMvaW1hZ2VfMTc1MDUxNDYxODQ4NV8wLnBuZyI6eyJjb25maWciOnsiaGlkZUFsbFRlc3RPbmUiOmZhbHNlfSwiZWxlbWVudHMiOlt7ImxlZnQiOjE2NS45NTY1MTg2NTE2NjgsInRvcCI6OTY5LjI2MTkzMjI3Mjc4NTEsIndpZHRoIjoxODcuODQ2NjE1ODY0ODQ1MiwiaGVpZ2h0IjozMTMuODMyNDU2NzU5NjQwMSwiYW5nbGUiOjAsImNJZCI6MX0seyJsZWZ0Ijo1NjguMDQyNDkzNzIxMzAxMiwidG9wIjoxMjU0LjQxNjI0MDY3Njc3NTUsIndpZHRoIjo1MDkuNzE3NzA4ODg2NDEzNDUsImhlaWdodCI6MTI5LjkwMzUwOTYzNDg3NDM1LCJhbmdsZSI6MCwiY0lkIjoyfSx7ImxlZnQiOjEzNDcuODg5NDc4MzE0MDk3NSwidG9wIjoxMjU0LjQwNTA5NDg3NjE1MTUsIndpZHRoIjo1OTUuNzc4OTU2NjI4MTk1MSwiaGVpZ2h0IjoxNDMuMjA0NjU0OTE5MjU0MzgsImFuZ2xlIjowLCJjSWQiOjN9LHsibGVmdCI6MTAwMS41ODg0MzMxODAwMzA1LCJ0b3AiOjk2OS42Mjc3NzcyNDY0NzQ3LCJ3aWR0aCI6MTM0MS42ODQ4NTk1OTAzMzI3LCJoZWlnaHQiOjMzOS43NDc2NDA1ODM1MTY2LCJhbmdsZSI6MCwiY0lkIjo0fSx7ImxlZnQiOjEzNTguODg5NDc4MzE0MDk3MiwidG9wIjozMjEuMzI0NDU2ODQ3NjYwNSwid2lkdGgiOjY0MC40MDg3MjI0OTU3MDAyLCJoZWlnaHQiOjM5Ny4yNzQ2NTEwMTc3MzEzNCwiYW5nbGUiOjAsImNJZCI6NX0seyJsZWZ0IjoxOTMuNjc1MTU1ODg2NzAwNzYsInRvcCI6NTQxLjc3NDYzODcyMDc3NTYsIndpZHRoIjoyMzkuMDE2OTY2NzgyNzg3NTMsImhlaWdodCI6NDM2LjAxODAxNTE1NDExMzEsImFuZ2xlIjowLCJjSWQiOjZ9XX19- [:span]
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 6
hl-color:: yellow
- [:span]
输入部分
[[Static Covariate Encoders]] 通过 GRN 将静态特征编码变成 4 个不同向量
动态特征 #card
post inputs
known future inputs
[[Variable Selection Networks]] 通过选择重要的特征,减少不必要的噪音输入,以提供模型性能。 #card
- [[GLU]] 灵感来自 LSTM 的门控机制,sigmoid 取值范围 0-1
对不同类型的输入变量应该区别对待 #card
静态变量通过特殊的 [[Static Covariate Encoders]],后续做为 encoder 和 decoder 的输入
过去的动态时变变量+动态时不变变量进入 encoder 结构中(蓝色 variable seletcion)
未来的动态时不变变量进入 decoder 结构中
seq2seq with teacher forcing 架构 #card
encoder 部分动态特征 embedding 和静态特征 embedding concat 在一起做为输入
- 静态变量 + 动态时变变量
decoder
- 静态变量 + 动态时不变变量
模型组成
[[Gated Residual Network]] 模型能够灵活地仅在需要时应用非线性处理 #card
外生输入和目标之间的确切关系通常是事先未知的,因此很难预见那些变量是相关的。
很难确定非线性处理的程度该多大,并且可能存在更简单的模型就能满足需求。
[[Temporal Fusion Decoder]] 学习数据集中的时间关系
通过 dense 层得到多个 [[Quantile Outputs]] #card
- $\hat{y}(q, t, \tau)=\boldsymbol{W}_q \tilde{\boldsymbol{\psi}}(t, \tau)+b_q$
[[TFT Interpretability Use Cases]] #card
输入特征重要性 examining the importance of each input variable in prediction
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 17
hl-color:: yellow可视化当前时间模式 visualizing persistent temporal patterns
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 17
hl-color:: yellow识别导致任何导致时间动态显著变化的时间 identifying any regimes or events that lead to significant changes in temporal dynamics
ls-type:: annotation
hl-page:: 17
hl-color:: yellow
[[Ref]]
[[@A Multi-Horizon Quantile Recurrent Forecaster]]